How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to breathtaking aerial photography, efficient surveying, and even exciting recreational pursuits. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding drone regulations and components to mastering advanced flight techniques and ensuring optimal maintenance. We’ll navigate the complexities of flight controls, explore diverse drone functionalities, and equip you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
From pre-flight checks and calibrations to capturing stunning aerial footage, we’ll break down each step into manageable, easy-to-understand instructions. Whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide serves as your roadmap to safe and proficient drone operation.
Drone Regulations and Safety: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety procedures. This section Artikels crucial legal requirements and safety protocols for safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Regulations in Various Locations
Drone regulations vary significantly depending on location. Urban areas often have stricter rules regarding flight altitude and proximity to people and buildings than more rural settings. National parks frequently have specific restrictions or require permits for drone operation to protect wildlife and natural resources. Always check local regulations before flying.
Drone Flight Safety Procedures
Prioritizing safety is paramount. A comprehensive approach encompassing pre-flight checks, in-flight vigilance, and post-flight procedures is crucial.
- Before Flight: Check weather conditions, ensure battery is fully charged, inspect drone for any damage, and confirm GPS signal strength.
- During Flight: Maintain visual line of sight, avoid flying near people or obstacles, be mindful of airspace restrictions, and never fly beyond your skill level.
- After Flight: Secure the drone, power it down, inspect for damage, and store it properly.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist

A thorough pre-flight inspection is essential for safe operation. This checklist helps ensure all systems are functioning correctly before commencing a flight.
- Battery charge level
- Propeller condition and securement
- GPS signal strength and accuracy
- Gimbal functionality (if applicable)
- Camera settings (if applicable)
- Remote controller connectivity
- Visual inspection for any physical damage
Comparison of Drone Regulations
The following table compares drone regulations across three countries. Note that these are simplified examples and specific regulations can be complex and change. Always consult official sources for the most up-to-date information.
| Country | Maximum Altitude | Registration Requirement | Specific Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 400 feet (generally) | Depends on drone weight and use | No flight over people, near airports without authorization |
| Canada | 400 feet (generally) | Registration required for most drones | No flight over people, near airports without authorization, restricted airspace |
| United Kingdom | 400 feet (generally) | Registration required for most drones | No flight over people, near airports without authorization, restricted airspace |
Understanding Drone Components and Functions
Understanding the key components of a drone and their functions is essential for safe and effective operation. This section details the core elements and their roles in flight.
Key Drone Components and Their Functions, How to operate a drone
A typical drone comprises several interconnected components working in harmony to achieve flight. These components are crucial for understanding drone functionality.
- Frame: Provides structural support for all other components.
- Motors: Power the propellers, generating thrust for flight.
- Propellers: Generate lift and control the drone’s movement.
- Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): Regulate the speed of each motor.
- Battery: Provides power to the entire system.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, responsible for stability and control.
- GPS Module (optional): Enables precise positioning and autonomous flight modes.
- Camera (optional): Captures images and videos.
- Remote Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements.
Drone Propeller Types and Flight Performance
Different propeller designs affect flight performance. Propeller size, pitch, and material influence thrust, speed, and efficiency.
- Larger propellers: Generate more thrust, suitable for heavier payloads.
- Higher pitch propellers: Produce more speed but may require more power.
- Material: Carbon fiber propellers are lighter and stronger than plastic ones.
Flight Controller Function and Drone Stabilization
The flight controller is the central processing unit of a drone, responsible for maintaining stability and executing pilot commands. It integrates data from various sensors to ensure smooth and controlled flight.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures acceleration and rotation.
- Barometer: Measures altitude.
- GPS (if equipped): Provides location data for precise positioning.
Diagram of Internal Drone Components
Imagine a central flight controller board at the heart of the drone, connected to each motor via the ESCs. The battery provides power to the entire system. The GPS module (if present) feeds location data to the flight controller. The camera (if present) is typically mounted on a gimbal for stabilized footage. All these components are securely mounted within the drone’s frame.
Pre-Flight Setup and Calibration
Proper pre-flight setup and calibration are crucial for safe and reliable drone operation. This section details the necessary steps for preparing your drone for flight.
Charging and Calibrating Drone Batteries
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow instructions carefully. Calibrating the battery ensures accurate voltage readings, maximizing flight time and safety.
- Connect the battery to the charger.
- Monitor the charging process; avoid overcharging.
- Once fully charged, disconnect the battery.
- (Calibration varies by drone model; consult your manual.)
Connecting Drone to Remote Controller and Mobile App
Connecting the drone to the remote controller and mobile app (if applicable) establishes communication and control. Ensure both devices are properly paired and have a strong signal.
- Power on the remote controller.
- Power on the drone.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for pairing the drone and remote controller.
- If using a mobile app, download and install it, then connect to the drone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
Pre-Flight GPS and Sensor Check
Before flight, verify that the drone’s GPS and sensors are functioning correctly. A strong GPS signal is essential for accurate positioning and stable flight in GPS modes.
- Ensure sufficient satellite signals are acquired.
- Check the compass calibration (if necessary).
- Verify that all sensors are reporting accurate data.
Pre-Flight Preparation Checklist
This checklist ensures all essential pre-flight preparations are completed before takeoff.
- Fully charged battery
- Strong GPS signal
- Remote controller connectivity
- Propeller inspection
- Visual inspection for damage
- Review of flight plan and local regulations
Basic Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section details the fundamental controls and maneuvers.
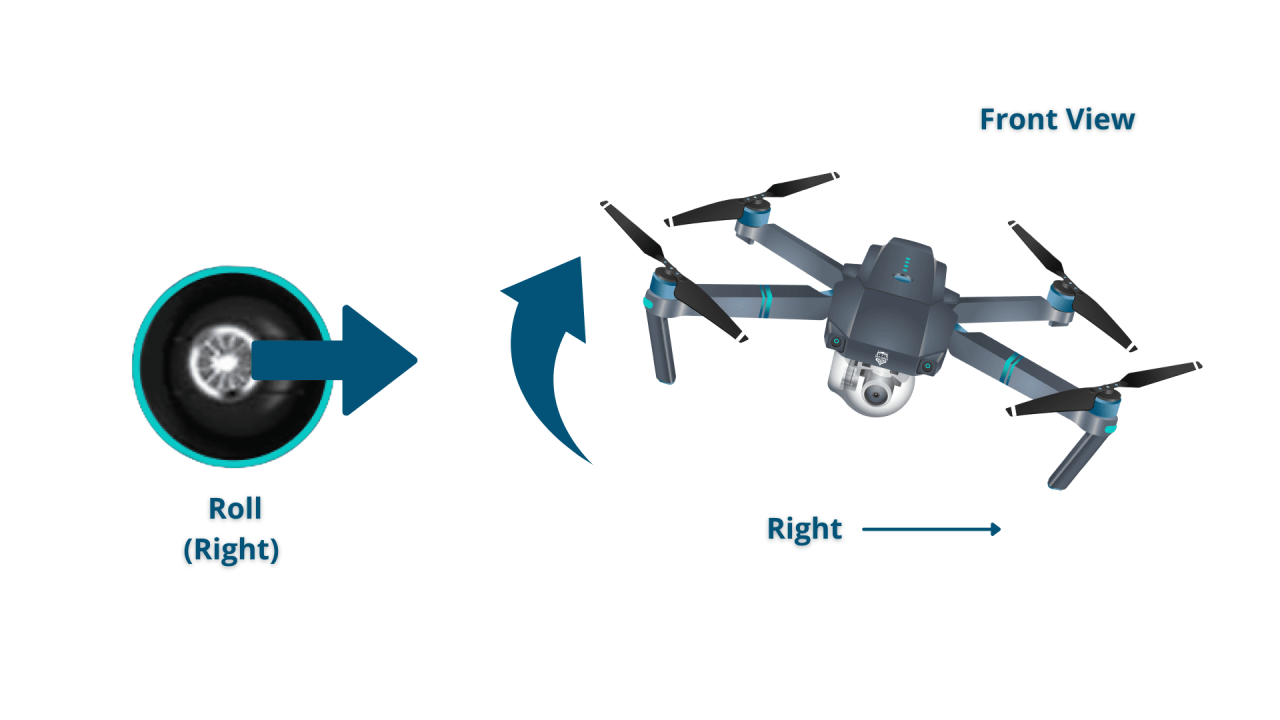
Basic Flight Controls (Throttle, Pitch, Roll, Yaw)
These four controls govern the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space.
- Throttle: Controls altitude (up and down).
- Pitch: Controls forward and backward movement.
- Roll: Controls left and right movement.
- Yaw: Controls rotation (turning).
Drone Flight Modes (Altitude Hold, GPS Mode, Attitude Mode)
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a constant altitude.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for precise positioning and autonomous flight.
- Attitude Mode: Provides more direct control, but requires more skill to maintain stability.
Basic Flight Maneuvers (Takeoff, Landing, Hovering, Directional Movement)
These maneuvers form the foundation of drone piloting.
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle until the drone lifts off.
- Landing: Slowly decrease throttle until the drone touches down gently.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady altitude and position.
- Directional Movement: Use pitch, roll, and yaw to move the drone in the desired direction.
Common Flight Errors and Corrections
Understanding common errors and their corrections is vital for safe flight.
- Drift: Caused by wind; compensate with control inputs.
- Sudden drops in altitude: Check battery level and GPS signal.
- Unresponsive controls: Check for controller connection and interference.
- Propeller failure: Land immediately; inspect propellers.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers and techniques for experienced pilots.
Advanced Maneuvers (Orbiting, Waypoint Following, Aerial Photography)
Advanced techniques enhance the capabilities of drone operation.
- Orbiting: Requires precise control to circle a subject smoothly.
- Waypoint Following: Pre-programmed flight paths for automated maneuvers.
- Aerial Photography: Utilizing various camera angles and flight paths for optimal shots.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires increased skill and caution. Maintain a steady hand and adjust controls to counteract wind gusts.
Flight Control System Comparison

Different flight controllers offer varying levels of stability and features. Some may offer more advanced autonomous flight modes or sensor integration.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Missions
Planning complex missions involves careful consideration of waypoints, altitude, and potential obstacles. Pre-flight simulation can be beneficial.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding key techniques and camera settings.
Tips and Techniques for High-Quality Aerial Media
Proper techniques ensure stunning visuals.
- Smooth movements: Avoid jerky camera movements.
- Optimal lighting: Shoot during the golden hour for best light.
- Composition: Use the rule of thirds for balanced shots.
Importance of Lighting and Composition
These factors significantly influence the quality of your aerial media.
Camera Settings (Aperture, Shutter Speed, ISO)
Understanding these settings is crucial for optimal image quality.
- Aperture: Controls depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Controls motion blur.
- ISO: Controls image sensitivity to light.
Common Camera Angles and Shots
These angles add variety and visual interest.
- High-angle shots: Show a wide view of the landscape.
- Low-angle shots: Emphasize the size and scale of subjects.
- Tracking shots: Follow a moving subject.
- Orbital shots: Circle around a subject.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in top condition.
Regular Drone Maintenance Tasks
These tasks ensure your drone’s longevity and safe operation.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and familiarity with its features, which can be enhanced by following comprehensive guides. For a detailed explanation of the process, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and effective operation. Mastering the skills to operate a drone opens up a world of possibilities for aerial photography and videography.
- Inspect propellers for damage: Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- Clean the drone body: Remove dirt and debris.
- Check battery health: Ensure batteries are properly stored and charged.
- Firmware updates: Keep the drone’s firmware up-to-date.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues saves time and prevents frustration.
- Low battery: Charge the battery.
- GPS signal loss: Find an area with a clear view of the sky.
- Motor failure: Inspect motors and ESCs for damage.
- Controller connection issues: Check batteries and ensure proper pairing.
Cleaning and Storing a Drone
Proper cleaning and storage prolong the drone’s lifespan.
- Clean the drone body with a soft cloth: Avoid harsh chemicals.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place: Protect it from dust and moisture.
- Store batteries separately: Avoid short circuits.
Common Drone Problems, Causes, and Solutions
This table summarizes common issues, their causes, and potential solutions.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructions, weak signal, faulty GPS module | Find open area, check satellite visibility, replace GPS module (if necessary) |
| Unstable flight | Wind, low battery, faulty sensors | Find calmer conditions, charge battery, calibrate sensors |
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has equipped you with the fundamental understanding of drone regulations, components, flight controls, and maintenance procedures. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety protocols are paramount. As you gain confidence and experience, explore advanced techniques and expand the creative possibilities of aerial flight.
Safe and responsible drone operation not only ensures your safety but also protects the airspace and surrounding environment. So, take to the skies, and capture your world from a new perspective!
FAQ Section
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration is typically needed after significant impacts or if the drone’s performance seems erratic. Consult your drone’s manual for specific recommendations.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
Immediately switch to a lower altitude mode (if available) and carefully bring the drone back to the starting point. Avoid attempting complex maneuvers without a strong GPS signal.
How do I handle strong winds while flying a drone?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the intricacies of flight controls and understanding how to safely maneuver the aircraft. For a comprehensive guide covering all these essential steps, I highly recommend checking out this resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight.
Proper training ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Avoid flying in high winds. If unexpected winds arise, reduce altitude and return to your starting point slowly and cautiously.
